pygeoapi kubernetes implementation - step 1 - manual deployment
Table of Contents
Introduction
pygeoapi kubernetes series introduction
Manual deployment of pygeoapi
Connecting to WSL and starting Minikube
wsl -d ubuntu
minikube status # Check that minikube is stopped.
minikube start --driver=docker # Start minikube
Launching the dashboard (optional)
The dashboard opens a web interface that allows you to view and interact with Minikube.
minikube dashboard
This command will launch a foreground process (the proxy server). You should therefore leave this command running and open a new terminal to continue:
wsl -d ubuntu
Deployment of a pygeoapi instance
Create a Kubernetes Deployment named pygeoapi using the official Pygeoapi Docker image.
kubectl create deployment pygeoapi --image=geopython/pygeoapi
This command automatically creates a ReplicaSet with one Pod by default. The created objects can be listed with the following command:
kubectl describe deployment pygeoapi
# Example :
Name: pygeoapi
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 19 May 2025 12:20:25 +0200
Labels: app=pygeoapi
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
Selector: app=pygeoapi
Replicas: 1 desired | 1 updated | 1 total | 1 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: app=pygeoapi
Containers:
pygeoapi:
Image: geopython/pygeoapi
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Environment: <none>
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: pygeoapi-78795f78b5 (1/1 replicas created)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 14m deployment-controller Scaled up replica set pygeoapi-78795f78b5 from 0 to 1
Or from the dashboard:
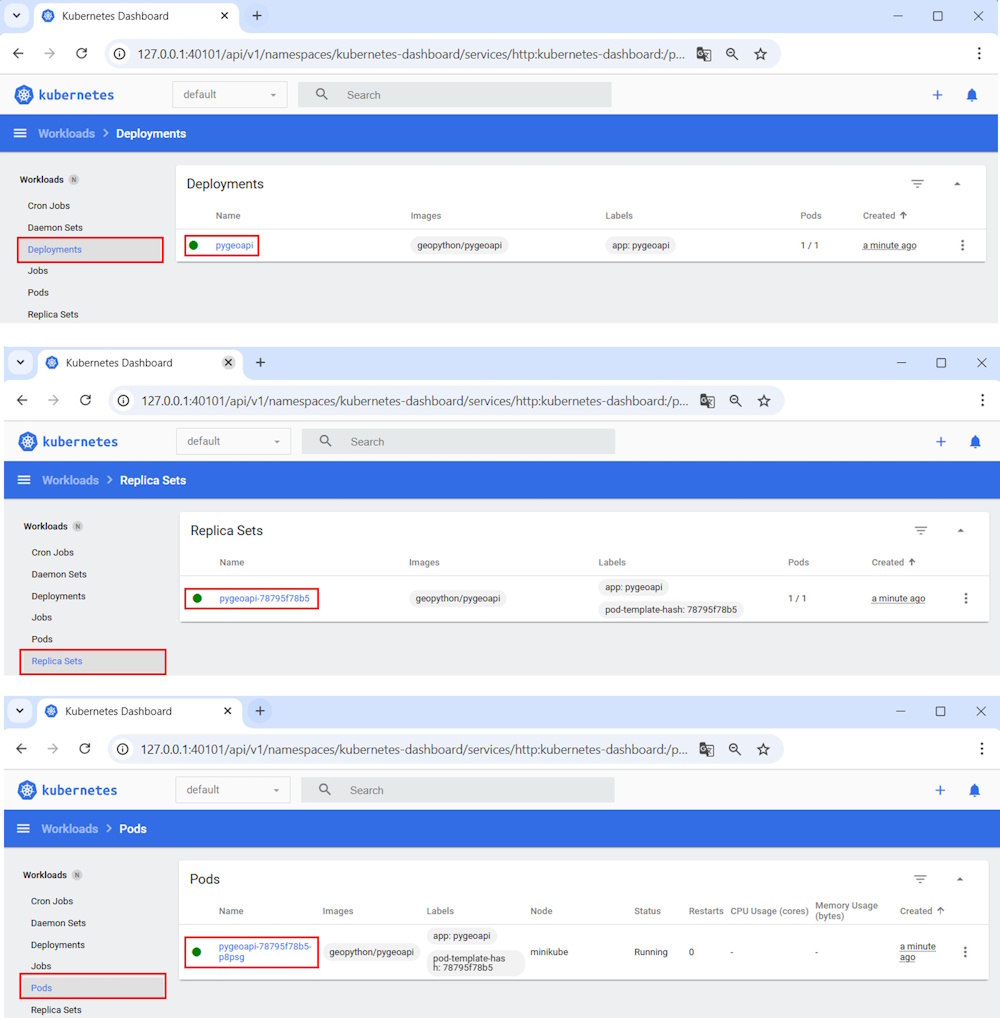
Pygeoapi is deployed but not yet accessible from a browser. You now need to expose the service on target port 80. Port 80 is the port on which the Pygeoapi WSGI server (Gunicorn by default) listens for requests.
Expose pygeoapi deployment
Run the command:
kubectl expose deployment pygeoapi --type=NodePort --port=80
The service is visible from the dashboard:
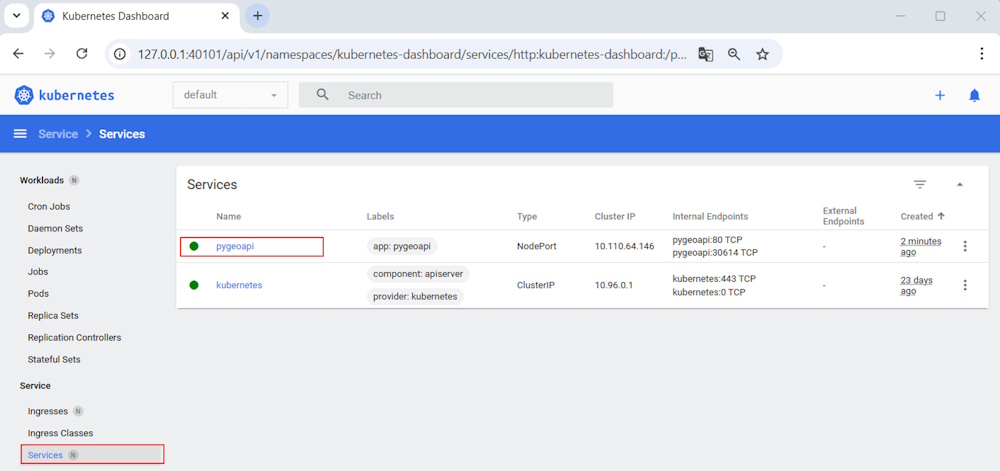
The Kubernetes cluster exposes the service and makes it accessible on a port automatically assigned in the range 30000–32767. The following command lets you find out the service’s URL:
minikube service pygeoapi
# Example:
|-----------|----------|-------------|---------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL |
|-----------|----------|-------------|---------------------------|
| default | pygeoapi | 80 | http://192.168.49.2:30614 |
|-----------|----------|-------------|---------------------------|
🏃 Starting tunnel for service pygeoapi.
|-----------|----------|-------------|------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL |
|-----------|----------|-------------|------------------------|
| default | pygeoapi | | http://127.0.0.1:40051 |
|-----------|----------|-------------|------------------------|
🎉 Opening service default/pygeoapi in default browser...
👉 http://127.0.0.1:40051
❗ Because you are using a Docker driver on linux, the terminal needs to be open to run it.
Pygeoapi is accessible, but something isn’t working correctly:
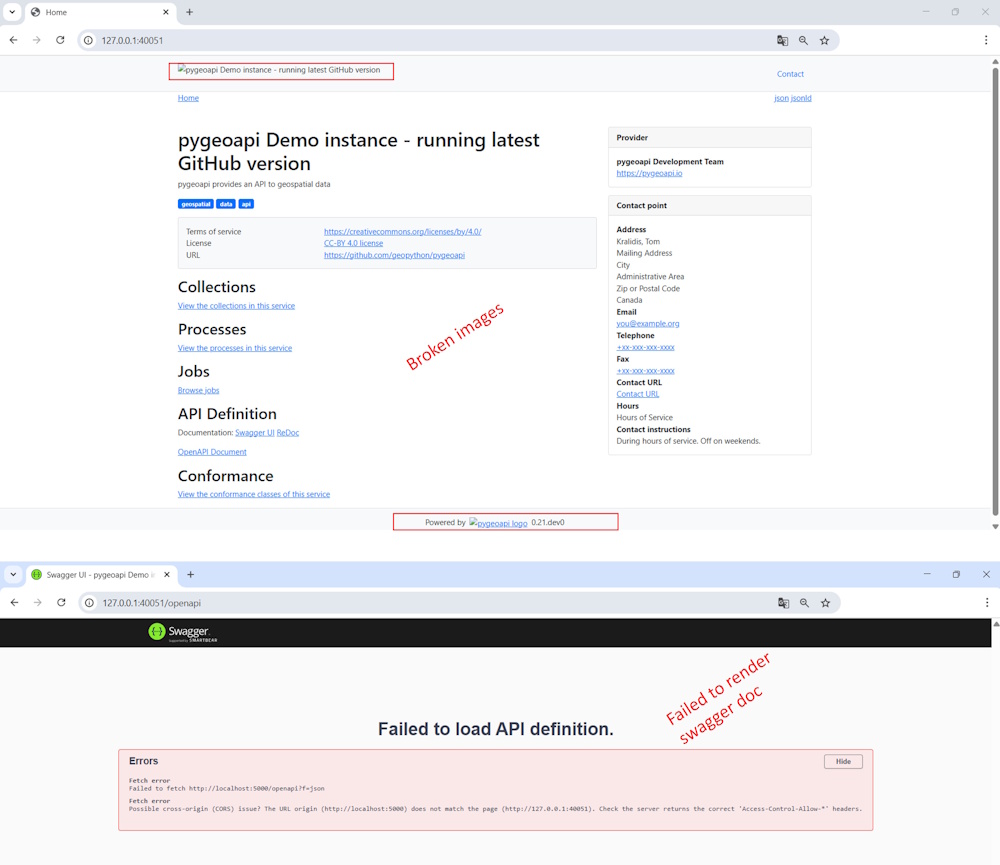
The issue stems from the fact that pygeoapi can be exposed via a proxy but needs to know the external URL from which it’s being called. By default, this URL is set to 0.0.0.0:5000. You can configure this URL in the pygeoapi configuration file. For now, we’re using the default settings, where the expected external URL is on port 5000.
Port forward
The following command forwards traffic from port 5000 on your local machine to port 80 of the pods managed by the pygeoapi deployment:
kubectl port-forward deployment/pygeoapi 5000:80
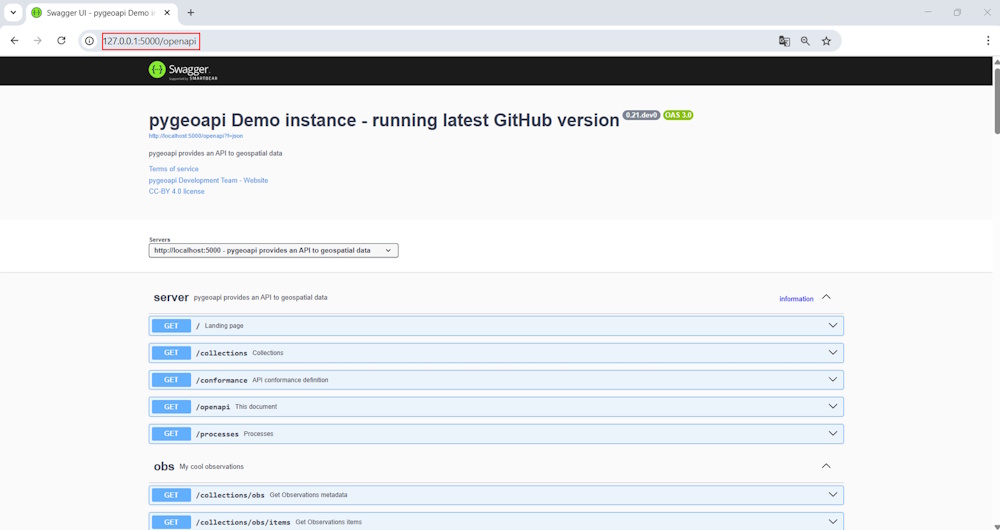
The Swagger documentation of pygeoapi now displays correctly from port 5000.
Conclusion
This first article illustrates a manual deployment of pygeoapi on Kubernetes and helps you understand the parameters expected by pygeoapi to display the application correctly. The next step is to automate the deployment using Kubernetes manifests and externalize the pygeoapi configuration file to enable parameter customization — a necessary step to expose your services.
You can now delete the deployment.
kubectl delete service pygeoapi
kubectl delete deployment pygeoapi